Introduction
Automated Facial Expression Recognition (FER) in the wild using deep neural networks is still challenging due to intra-class variations and inter-class similarities in facial images. Deep Metric Learning (DML) is among the widely used methods to deal with these issues by improving the discriminative power of the learned embedded features. This paper proposes an Adaptive Correlation (Ad-Corre) Loss to guide the network towards generating embedded feature vectors with high correlation for within-class samples and less correlation for between-class samples. Ad-Corre consists of 3 components called Feature Discriminator, Mean Discriminator, and Embedding Discriminator. We design the Feature Discriminator component to guide the network to create the embedded feature vectors to be highly correlated if they belong to a similar class, and less correlated if they belong to different classes. In addition, the Mean Discriminator component leads the network to make the mean embedded feature vectors of different classes to be less similar to each other.We use Xception network as the backbone of our model, and contrary to previous work, we propose an embedding feature space that contains k feature vectors. Then, the Embedding Discriminator component penalizes the network to generate the embedded feature vectors, which are dissimilar.We trained our model using the combination of our proposed loss functions called Ad-Corre Loss jointly with the cross-entropy loss. We achieved a very promising recognition accuracy on AffectNet, RAF-DB, and FER-2013. Our extensive experiments and ablation study indicate the power of our method to cope well with challenging FER tasks in the wild.
Architecture
FD component is proposed to improve the discriminative power of the embedded feature vectors that are defined in the embedding feature space. Moreover, monitoring the performance of the network during the training process and updating the proposed Adaptive Attention Map forces the model to perform accurately for dramatically imbalanced datasets.
our proposed architecture contains k different embedded feature vectors being defined in a so-called embedding space. Particularly, we define k the same as the numbers of the facial expressions (which is 7 in this paper), and thus for an input image, the model creates 7 independent embedded feature vectors. Since there is no relation between the embedded feature vectors generated for and input
image I, there is no guarantee that the different embedded feature vectors represent different features of I. Consequently. we proposed the ED component of Ad-Corre Loss to force the model to generate the embedded feature vectors which are as less correlated to each other as possible. In other words, the ED component is designed to guide the model to generate the embedded feature vectors representing different features from an input image.

We propose MD component in the Ad-Corre Loss to make the network generate the embedded feature vectors such that
the means of different classes are uncorrelated. As Fig shows, MD component is calculated for each of the k embedded feature vectors in the embedding space.

Evaluation and Samples
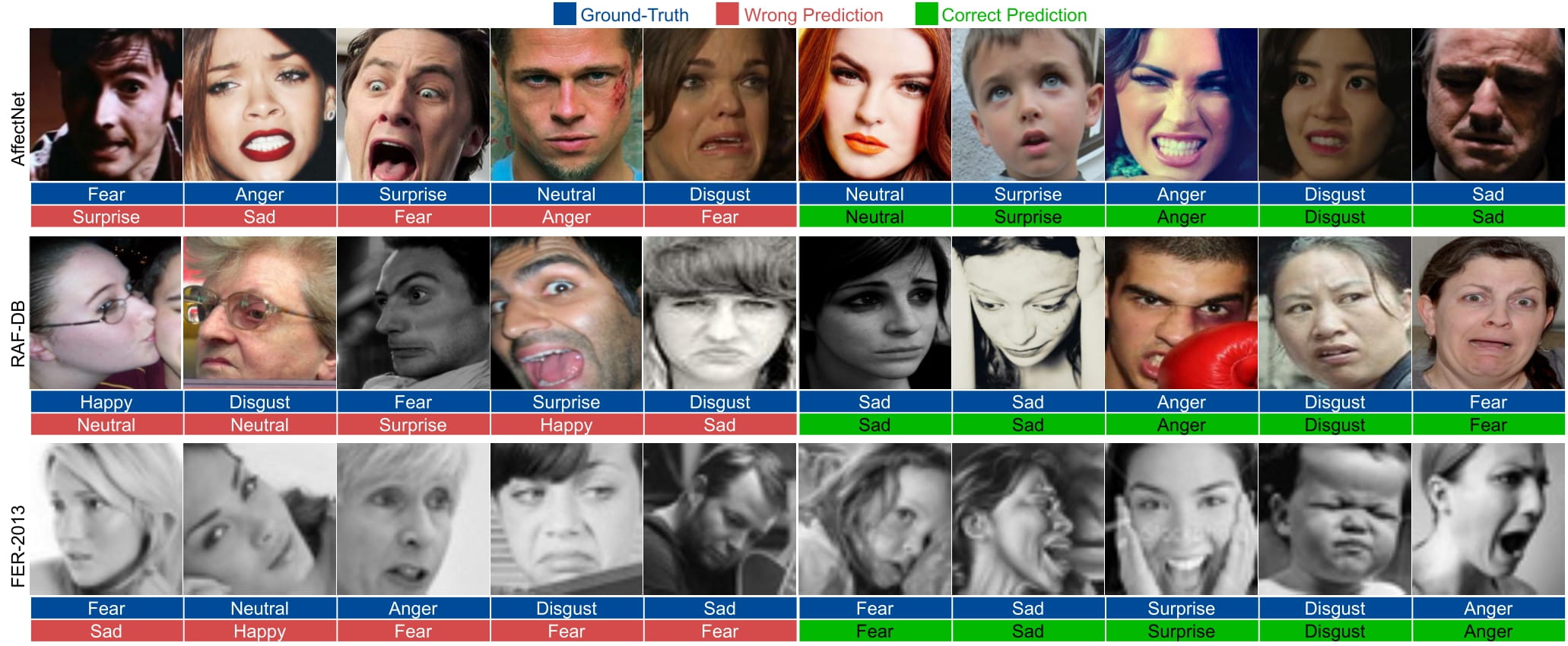
The following samples are taken from the paper:
Installing the requirements
In order to run the code you need to install python >= 3.5. The requirements and the libraries needed to run the code can be installed using the following command:
pip install -r requirements.txt
Using the pre-trained models
The pre-trained models for Affectnet, RafDB, and Fer2013 are provided in the Trained_Models folder. You can use the following code to predict the facial emotionn of a facial image:
tester = TestModels(h5_address='./trained_models/AffectNet_6336.h5')
tester.recognize_fer(img_path='./img.jpg')
Training Network from scratch
The information and the code to train the model is provided in train.py:
trainer = TrainModel(dataset_name=DatasetName.affectnet, ds_type=DatasetType.train_7)
trainer.train(arch="xcp", weight_path="./")
Reference:
@ARTICLE{9727163,
author={Fard, Ali Pourramezan and Mahoor, Mohammad H.},
journal={IEEE Access},
title={Ad-Corre: Adaptive Correlation-Based Loss for Facial Expression Recognition in the Wild},
year={2022},
volume={},
number={},
pages={1-1},
doi={10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3156598}}


